Zoom security: What you need to know about meeting privacy
Many students, remote workers, and teams rely on Zoom as their go-to video call platform. But, like many widely adopted communication services, its users need to consider privacy and security.
In this guide, we’ll explore the security considerations when using Zoom, how the platform’s security has evolved, how it handles your data, and what you can do to keep your meetings secure and private.
Zoom security and privacy considerations
Zoom, like other video conferencing platforms, may present certain risks, depending on how its features are configured and used. Understanding them can help you keep meetings more secure.
Unauthorized access
Unauthorized access happens when someone joins a Zoom session they weren’t invited to, often by using leaked login credentials or unprotected meeting links. In some cases, attackers may use previously stolen email and password combinations to guess Zoom account passwords.
Meeting hijacking (Zoom bombing)
Meeting hijacking, also known as Zoom bombing, is a specific type of unauthorized access where uninvited users join a Zoom call and disrupt it with offensive content, slurs, or illicit material.
These attacks can occur from disabling Zoom’s Waiting Room feature, which allows admins to vet participants before entering the meeting. Skipping meeting passcodes and sharing links broadly could also enable Zoom bombing attacks.
Exposed or publicly shared Zoom meeting links
Zoom meetings are only as secure as the link-sharing practices around them. When links are posted publicly on social media or forums, they can become easy targets for disruption or eavesdropping.
Zoom phishing emails
Attackers may use domains that contain the word "zoom" to send phishing emails disguised as Zoom meeting invites. These emails may contain links to fraudulent websites designed to download malware or steal data.
Learn more: How to delete your Zoom account
The evolution of Zoom’s security architecture
Like many platforms that experience fast growth, Zoom has been a target of attacks exploiting communication apps. However, Zoom has made a series of changes to its security and privacy practices in order to address past issues and attacks.
Here's a simple breakdown of the key improvements:
- The 90-day plan (2020): Zoom paused all new features for 90 days to focus its resources on security, which led to major updates like stronger default settings to stop uninvited guests from entering meetings.
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) with 256-bit keys in Galois/Counter Mode (GCM) (2020): With the release of Zoom 5.0, Zoom introduced AES 256-bit GCM encryption for all meetings. It’s the faster, modern default encryption with built-in authentication for better protection of data in transit.
- True end-to-end encryption (E2EE) rollout (2020–2021): To fix its encryption issues, Zoom acquired Keybase to build a true E2EE solution that allowed the meeting host to generate the encryption keys. This milestone was a part of Zoom’s 90-day security plan.
- Future-proofing with post-quantum E2EE (2024): Zoom rolled out post-quantum E2EE for meetings using the Kyber 768 algorithm to help protect users against “harvest now, decrypt later” attacks.
- Ongoing commitment: Zoom regularly releases security updates, publishes vulnerability disclosures, operates a bug bounty program, and undergoes independent security assessments. It has also expanded its controls for meeting hosts and organizations to reduce unwanted access and misuse.
Understanding Zoom’s encryption and data protection
Zoom lets hosts and account admins enable E2EE for meetings through the account or meeting settings. When this option is turned on, encryption keys are generated on participants’ devices instead of Zoom’s servers. This prevents anyone outside the meeting, including Zoom itself, from accessing the audio, video, or in-meeting chat content.
However, enabling E2EE disables several other features. Cloud recording, live streaming, polling, and joining by phone aren’t available when E2EE is active.
By default, Zoom meetings use standard encryption (256-bit AES GCM) for routine meetings. The company suggests using E2EE for highly sensitive conversations.
Zoom lets hosts verify that E2EE is active by checking the green shield with a padlock icon during a call. If the meeting isn’t end-to-end encrypted, the icon will show a green shield with a check mark instead. This makes it easier for you to confirm the protection level in real time.
That said, Zoom still collects certain metadata, even when E2EE is enabled. This includes:
- IP addresses for approximate location.
- Device and operating system details.
- Timestamps.
- Basic usage data, such as when participants join or leave a meeting.
How to secure your Zoom meetings

Turn on Waiting Room
Zoom’s Waiting Room is one of the most effective ways to prevent unwanted guests. It holds participants in a virtual lobby until you manually admit them, helping you screen who gets into your meeting. This is especially useful for meetings that involve sensitive topics or invite-only attendees. While it adds a small step to joining, it gives hosts full control over who enters and when.
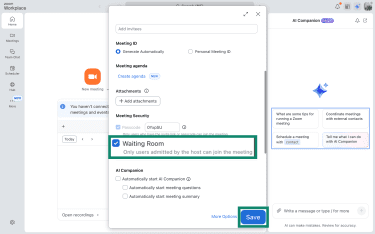
To enable Waiting Room:
- In your Zoom dashboard, select Schedule to open settings for a new meeting.
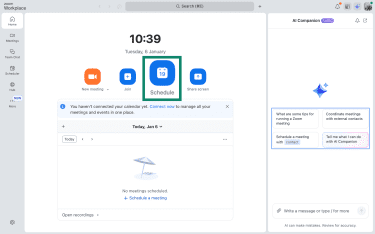
- Tick the box beside Waiting Room and click Save.
Avoid sharing meeting links
Your Zoom meeting link is like a digital key. If you post it publicly on social media, websites, or open forums, anyone can use it to try to join your call. This opens the door to unwanted disruptions, including meeting hijacking or eavesdropping.
Even if you use the Waiting Room feature, sharing your meeting too widely could lead to an overcrowded waiting room and more potential for intruders to slip through. It’s safer to keep your meeting link private and only share it with trusted participants.
Here are some best practices for link sharing:
- Send invitations directly via email or calendar invites.
- Avoid posting links on public platforms (if feasible).
- If you need to post publicly, require registration or authentication to join.
- Always double-check invite lists before sending.
Keep your Personal Meeting ID private
Your Personal Meeting ID (PMI) is a static virtual meeting room tied to your account. Since it never changes, anyone who has it can attempt to join your meetings, especially if you’ve used it multiple times across different events or platforms. Treat it like a phone number or password and don’t share it unless necessary.
Instead, generate a unique meeting ID each time you schedule a call. It’s also a good idea to avoid posting your PMI on social media or public websites and to update old calendar invites that may still include it.
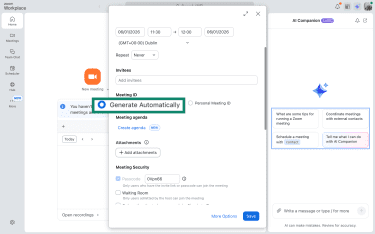
To automatically generate meeting IDs for every call:
- Click Schedule to open the meeting setup window.
- In the Meeting ID section, select Generate Automatically instead of Personal Meeting ID.
Customize privacy settings
Taking time to review your Zoom privacy settings helps you prevent accidental oversharing, reduce disruptions, and limit opportunities for abuse, especially in meetings with large or unfamiliar groups. You can disable features like screen sharing, private chat, or join before host to close loopholes that attackers often exploit.
Only allow authenticated users
Requiring authentication adds another layer of control over who can join your Zoom meetings. Instead of letting anyone with a link enter, this forces participants to sign into Zoom before joining.
This helps you keep track of attendees and prevent meeting links from being reused or shared with the wrong people. It’s especially useful for external meetings, webinars, or sessions that include sensitive discussions.
Here’s how to require authentication for meetings:
- Click Schedule to open the meeting setup window.
- Tick the box beside Only authenticated users can join: Sign in to Zoom.
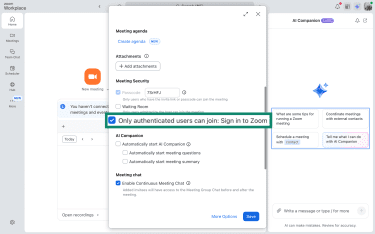
Note: On some devices, the setting to allow only authenticated users may be found in the web portal instead of the app. To turn this setting on, go to My Account > Settings and toggle it on.
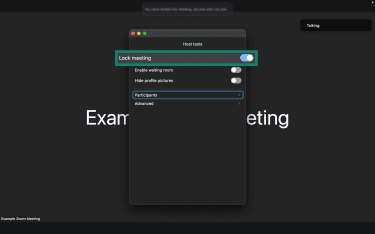
Lock your meeting
Locking your Zoom meeting stops anyone else from joining, even if they have the meeting ID and passcode. It’s a smart move for secure or sensitive sessions where you don’t expect any late arrivals. Once everyone’s in, locking the room ensures no one can sneak in unnoticed.
But there are a few things to keep in mind. If someone joins late or loses connection, they won’t be able to re-enter unless you manually unlock the meeting. You also won’t get notified if someone is blocked, which could lead to confusion. That’s why it’s best to lock your meeting only after confirming all expected participants are present.
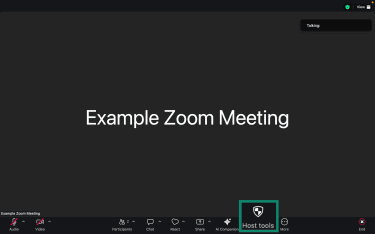
Here’s how to lock your meeting:
- After all your desired participants have joined the meeting, click on Host tools from the toolbar at the bottom of your Zoom window.
- Toggle the switch beside Lock meeting.
Train team members on Zoom security
If you run a team, make sure everyone understands how to keep Zoom meetings secure. Even the best settings won’t help if users don’t know how to use them. Human error is a common cause of security breaches, and a bit of training can make a big difference.
Teach your team the basics, like not sharing meeting links publicly, using unique meeting IDs, enabling the Waiting Room, and spotting phishing attempts. Hosts should also know how to lock a meeting, remove disruptive participants, and manage waiting rooms.
You can run short practice sessions or share a guide with screenshots and step-by-step instructions. With the right knowledge, your team becomes your first line of defense.
Use a VPN to secure your connection
Zoom encrypts your call content while it travels between your device and Zoom’s servers to prevent eavesdropping during the meeting. But that protection only applies to Zoom traffic. It doesn’t cover your other internet activity.
That’s where a virtual private network (VPN) adds value. A VPN encrypts all traffic leaving your device, not just Zoom, and routes it through a secure tunnel to a VPN server. This helps protect you from local network threats like packet sniffing (capturing data packets passing through a network), Domain Name System (DNS) spoofing (creating or sending forged DNS responses), or man-in-the-middle (MITM) attacks.
For example, if you’re on public Wi-Fi at a café, airport, or hotel, someone could attempt to intercept data or redirect your connection. A VPN blocks those attempts by keeping all your internet activity encrypted and private.
VPNs don’t replace Zoom’s built-in security, but they do add an additional layer of security to help keep your connection and data safer, especially in vulnerable environments.
FAQ: Common questions about Zoom security issues
Does Zoom still have security issues?
Yes, but not on the same scale as during the pandemic. While Zoom hasn’t experienced a major breach since 2020, new vulnerabilities still emerge from time to time. These can include bugs that expose session data or allow privilege escalation if users don’t update their software in time.
How can I secure my Zoom meetings?
You can protect your Zoom meetings by using built-in security features like the Waiting Room, which lets you control who joins before the meeting starts. It’s also a good idea to avoid sharing your meeting link publicly or sharing your Personal Meeting ID (PMI). Instead, use an automatically generated meeting ID.
What should I do if my meeting is Zoom bombed?
If a Zoom meeting that you are hosting is hijacked, the first step is to remove the disruptive participant using the in-meeting controls. You should then lock your meeting to prevent anyone else from joining and use the Suspend Participant Activities feature if available to pause all in-meeting interactions while you assess the situation. It’s important to report the incident to Zoom and review your settings afterward to help prevent it from happening again.
Is Zoom end-to-end encrypted (E2EE)?
Zoom supports E2EE, but it’s optional and must be turned on in your settings. When enabled, only meeting participants control the encryption keys, so not even Zoom can access the content. However, features like cloud recording and phone dial-in are disabled when you turn on E2EE.
What steps has Zoom taken to improve its security?
Since 2020, Zoom has improved its security. It required meeting passcodes for every meeting and enabled Waiting Rooms by default. End-to-end encryption (E2EE) became available to all users and was later upgraded with post-quantum protection in 2024. Zoom also runs a bug bounty program, publishes regular security updates, and undergoes independent audits.
Take the first step to protect yourself online. Try ExpressVPN risk-free.
Get ExpressVPN